High-frequency bolted RFID tags are usually used for identification and traceability of cylinder lines and cylinder head lines in machine shops.
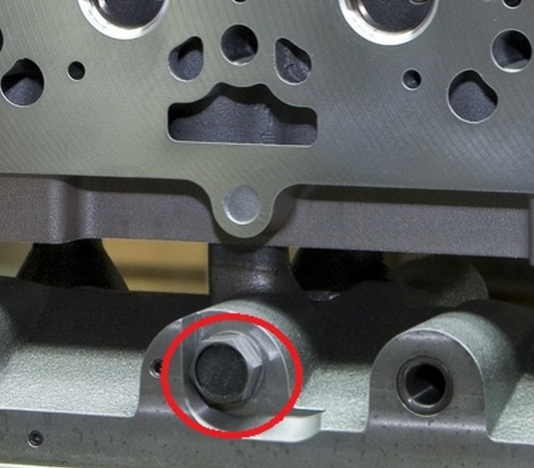
Bolt RFID tags usually have a variety of specifications, storage capacity up to 128KB, its appearance is very similar to ordinary bolts, as shown in the following red circle:
Take cylinder machining as an example. When the cylinder goes online, first install, tighten and write the RFID bolts into the work order and serial number information; when the cylinder passes through the key processing station, the PLC will key work information such as tightening value, leak test The test result is written into the bolt RFID; when the cylinder enters the next station, the PLC reads the RFID and checks the results of the previous process; when the cylinder goes offline, the PLC reads the RFID data and synchronizes it to the MES system.
In the complete manufacturing process of an engine, multiple RFID tags are used, such as:
Bolt RFID for cylinder frame
Bolt RFID for cylinder head frame
Tray RFID
Cylinder head separate tray RFID
Piston connecting rod separate tray RFID
Pallet RFID for external wiring
Truck engine Test Line pallet RFID
When the engine is transferred from the interior to the exterior, or when it needs to be repaired offline, because the engine and the tray are separated, it is necessary to backup and restore the RFID data and the MES, which is cumbersome.
Therefore, if the bolted RFID tags on the cylinder block can be used in the complete manufacturing process, there will be no problem of data transfer, and data exchange between MES and PLC can be greatly reduced, but it is faced with great difficulties.
Because of the small spacing between engine stations, high-frequency rather than ultra-high-frequency RFID technology is used. This results in RFID tags that have a short reading distance (typically <0.2 meters) and a small angle. Therefore, readers are generally required to face the tags tightly. Sticker installation.
Most of the cylinders are assembled inside the engine after being assembled. If the bolts are installed inside the RFID, it is difficult to identify them. If the bolts are installed on the outside, they may interfere with the parts and equipment during the assembly process and be difficult to identify.
Well, if we want to use the cylinder bolt RFID to track the entire process, we need to start with the design and work out a plan together with the process and control experts:
In the cylinder body design bolts RFID-specific process installation hole; This hole will not affect the engine rigidity, after Assembly also has been exposed to the outside of the engine, in the factory with ordinary bolts or rubber stopper for closure.
Bolt RFID in the cylinder machine installation, the whole process will not and other parts, equipment formation interference.
Equipment and OEM engineers, according to the location and angle of the bolt RFID, adjust the location of RFID Reader station. This scheme can effectively ensure the data security, but increases the complexity of the process, it is the pros and cons.
